Getting Started with ARC
Connecting to an ARC cluster
ARC systems are remote, meaning you must connect to them from your local machine. This is typically done using a secure shell (SSH) connection.
Before connecting, ensure you have:
- A terminal or SSH client installed (e.g., Terminal on macOS/Linux, PuTTY on Windows)
- Your CCDB system username and password
Step-by-step Connection Guide
- Open Your Terminal: On macOS or Linux, open the
Terminal. On Windows, useCommand Prompt,PowerShell, or an SSH client likePuTTY. -
Connect to the ARC cluster: To connect to the
Cedarsupercomputer, type the following command:ssh USERNAME@cedar.alliancecan.ca- Replace
USERNAMEwith your CCDB username. - To log into another ARC cluster, replace
cedarwith its name (narval,beluga, etc.)
- Replace
-
Enter your password: If you are not using
SSHkey authentication, you will be prompted to enter your password. - Authenticate using MFA: Follow the multi-factor authentication prompt (e.g.: approve the request on Duo).
HOME directory. Learn more about ARC storage locations.
Trouble Shooting
- If the
SSHconnection fails, ensure your internet connection is stable. - Verify that your username and password are correct.
- If using
SSH keys, confirm they are correctly configured.
Transferring Data
Tranferring data between your local computer and remote clusters is an important part of working with HPC systems. The method you choose depends on the size of the data, the systems involved, and the specific requirements of your project.
Login nodes have internet access, so commands such as curl or wget can be used to download files directly from the internet. The scp command is ideal for simple transfers between your personal computer and remote ARC clusters. For larger datasets or transfers between two ARC clusters, Globus provides high-speed, secure transfers, making it the best option for large-scale file transfers.
Using Command Line Tools (scp)
The scp command is used to securely copy files or directories between a local (your personal computer) and a remote (HPC cluster) host, or between two remote hosts. It uses SSH for data transfer and provides a secure way to transfer files over the network.
scp <source> <destination>
Copying a file from local to remote
scp myfile.txt user@remote_host:/path/to/remote/directory/
myfile.txt: The file you want to transfer from your local system.user@remote_host: Replaceuserwith your username on the remote system, andremote_hostwith the remote server’s address (it could be an IP address or domain name)./path/to/remote/directory/: The directory on the remote server where the file will be placed.
Copying a file from remote to local
scp user@remote_host:/path/to/remote/file.txt /path/to/local/directory/
Copying a directory from local to remote
scp -r my_directory/ user@remote_host:/path/to/remote/directory/
The -r flag (stands for recursive) tells scp to copy the entire directory and all its contents.
Using Globus
Globus is a fast, reliable, and user-friendly tool for secure file transfers. It allows you to easily move files between your personal computer and an ARC cluster or between two ARC clusters.
In Globus, a collection is a designated storage location that allows you to transfer and manage files. Collections can be hosted on HPC clusters, cloud storage systems, or personal computers, and provide a seamless way to move data across different systems.
Logging Into Globus
-
Go to the Alliance’s Globus Portal.
In the Use your existing organizational login box, select Digital Research Alliance of Canada.
Press Continue.
-
Log in using your CCDB username (not your email) and password.
-
Open File Manager in the Globus portal.

Transferring Files
-
Use the Search bar to find collections by name.
For example to transfer files to or from Narval, type
narvaland select theCompute Canada - Narvaloption.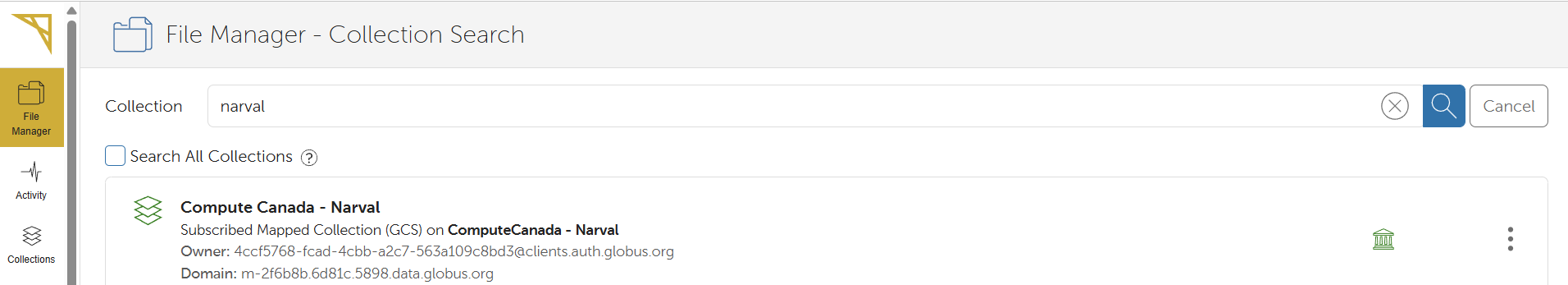
-
Once the collection is selected, you will see a ist of directories and files. Navigate them by double-clicking the folder or using the up one folder button.
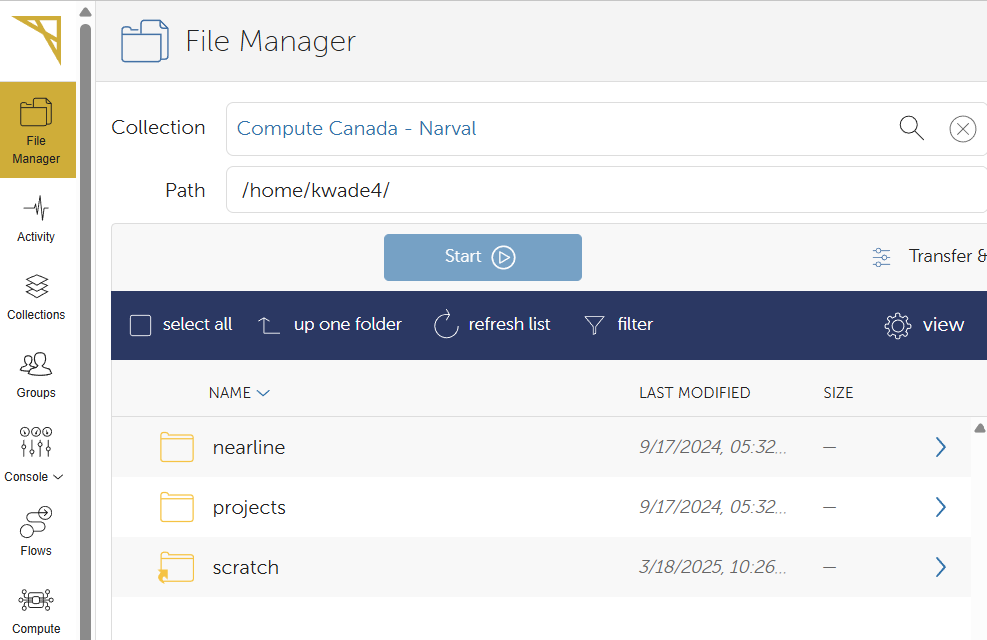
-
To start a transfer, select a file or directory by single-clicking. To select multiple files or directories, hold
Ctrl. -
Press the blue Start button to start the transfer.

-
Globus will assign a unique job ID, and the transfer will begin immediately.
-
To track the progress of your file transfer or view past transfers, click on Activity in the left sidebar.
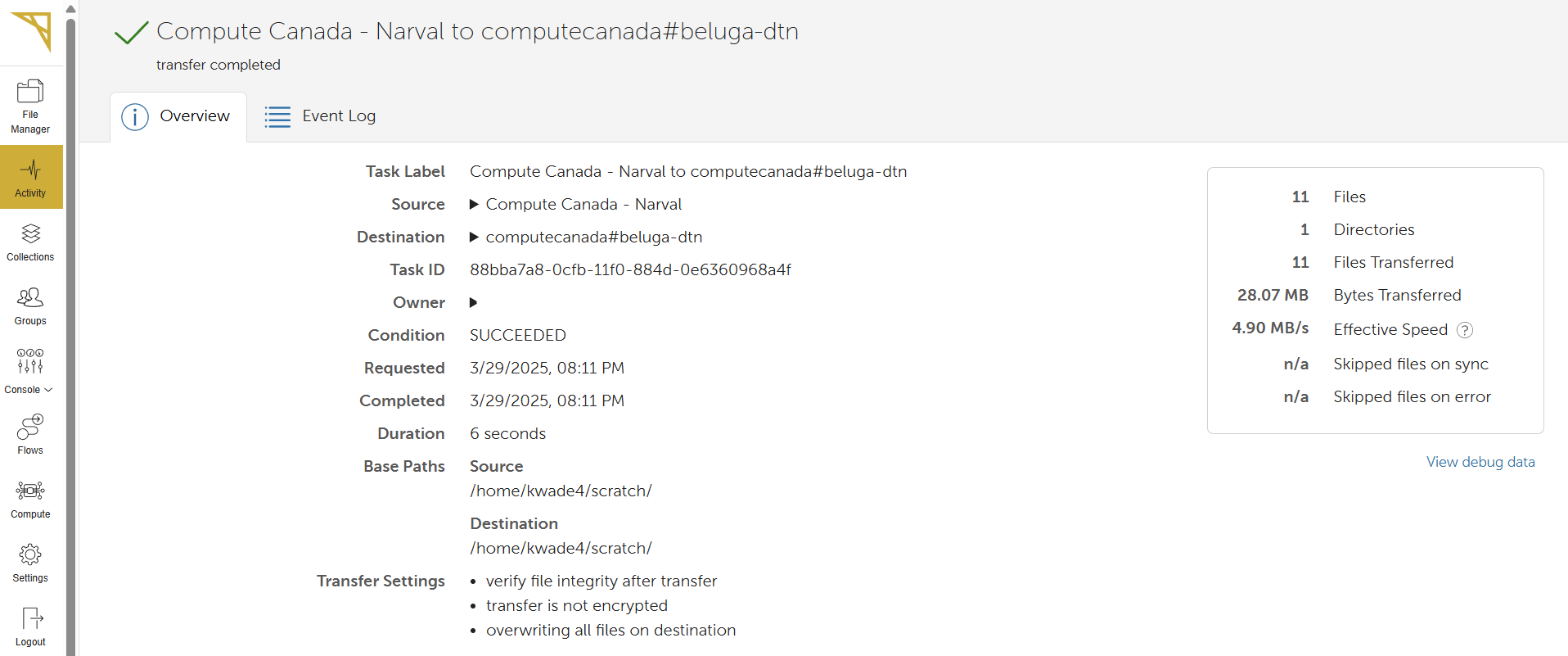
Once your transfer is complete, you will receive an email.
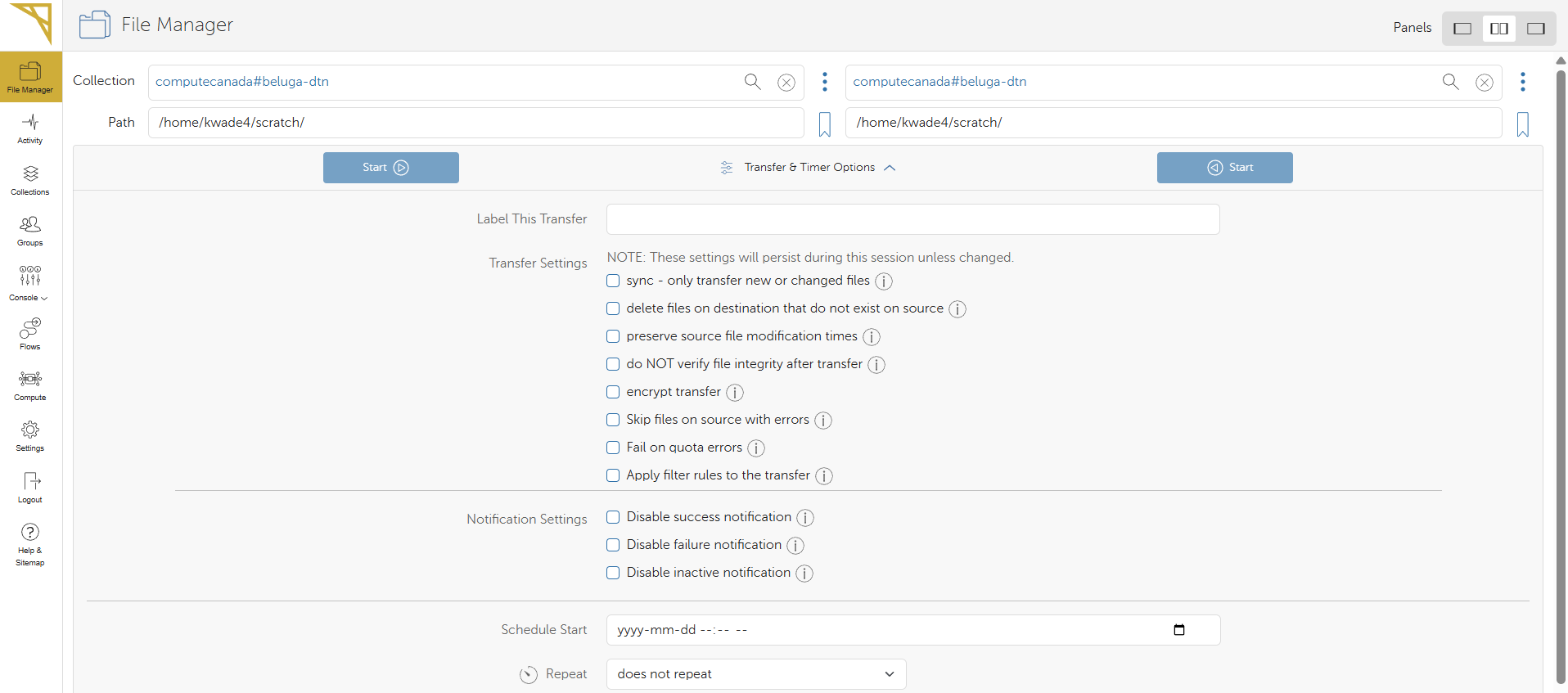
File Transfer Options
Globus also offers a variety of file transfer options through the Transfer & Sync Options button. These allow you to:
✅ Sync transfers (only move new or modified files)
✅ Delete destination files that don’t exist in the source
✅ Preserve file modification timestamps
✅ Verify file integrity after transfer (enabled by default)
✅ Encrypt the transfer (note: encryption is slow and should only be used only for sensitive)
For more details on using Globus, refer to the Alliance’s Globus Documentation page.
Using Python
When working with Python on ARC clusters, it’s best to set up a virtual environment (venv). This helps keep your Python code runs with the correct dependencies, no matter which compute node processes your job.
ARC clusters use wheels which are pre-compiled Python packages that are optimized or the clusters and help to speed up installation and reduce disk usage.
Setting Up a Python Virtual Environment
- Check which versions of Python are available.
module avail python - Load the desired Python version.
module load python/3.10 - Create a virtual environment.
virtualenv --no-download ENVThis command creates a new virtual environment called
ENV. The--no-downloadflag ensures that the wheels optimized for the ARC clusters are used. - Activate the virtual environment.
source ENV/bin/activate - Upgrade
pip.pip install --no-index --upgrade pipThis command updates pip to the latest version and the
--no-indexflag ensures that the ARC-optimized wheels are used. - Exit the virtual environment.
deactivate
Installing Python Packages
To install Python packages in your virtual environment, the best approach is to use wheels, which are optimized for the ARC clusters. This makes the installation process much faster and more efficient.
Recommended Method
Install packages using pip within your job script.
pip install --no-index <package_name>
The --no-index flag ensures that pip uses wheels, which are pre-compiled and tailored for ARC systems. This makes installation faster and helps conserve disk space in your /HOME directory.
Alternative Methods
If wheels are not provided for your Python package, you can install packages from GitHub or use the centralized web-based version of pip on the login node.
When using these alternative installation methods, in your job script, you need to create and activate your virtual environment in your \HOME directory:
source $HOME/ENV/bin/activate
Pre-installed Packages
ARC clusters come with a variety of pre-built Python wheels that are optimized for the cluster’s architecture, allowing for fast and efficient installations. These include popular libraries commonly used in scientific computing, machine learning, and bioinformatics. Some of the pre-installed packages include:
- PyTorch
- Biopython
- Scikit-learn (sklearn)
- Many more!
For convenience, the SciPy stack is available as a module:
- NumPy
- SciPy
- Matplotlib
- IPython
- pandas
- Sympy
- nose
To load the SciPy stack, use:
module load scipy-stack
Software Available
ARC clusters also have a variety of scientific software pre-installed from various disciplines. Some examples include:
| Discipline | Software |
|---|---|
| 🔬 Chemistry | RDKit, CP2K, LAMMPS, GROMACS, ABINIT, AMBER, Atomicrex |
| 🧬 Bioinformatics | Plink, REGENIE, Rosetta, IQ-Tree, Bowtie-2, Samtools, MUSCLE |
| ⚙️ Physics / Engineering | Quantum ESPRESSO, Abaqus, OpenFOAM, MESA, STAR-CCM |
| 🌍 Earth Sciences | CCSM, CDO, GRASS GIS, PROJ, QGIS |
For a complete list of available software, visit the Alliance’s Documentation.